Microsoft Azure Data Lake Gen2 network storage
This Network Storage uses Microsoft Azure Data Lake storage as additional storage space.
Adding the Microsoft Data Lake Gen2 Network Storage
In the desired domain, navigate to the ACCOUNTS > Network Storage module. Click Add. The Add Network Storage dialog displays. Select Microsoft Azure Data Lake Gen2 as the Protocol, then click on OK. The Add "Microsoft Azure Data Lake Gen2" Network Storage dialog displays as shown below.
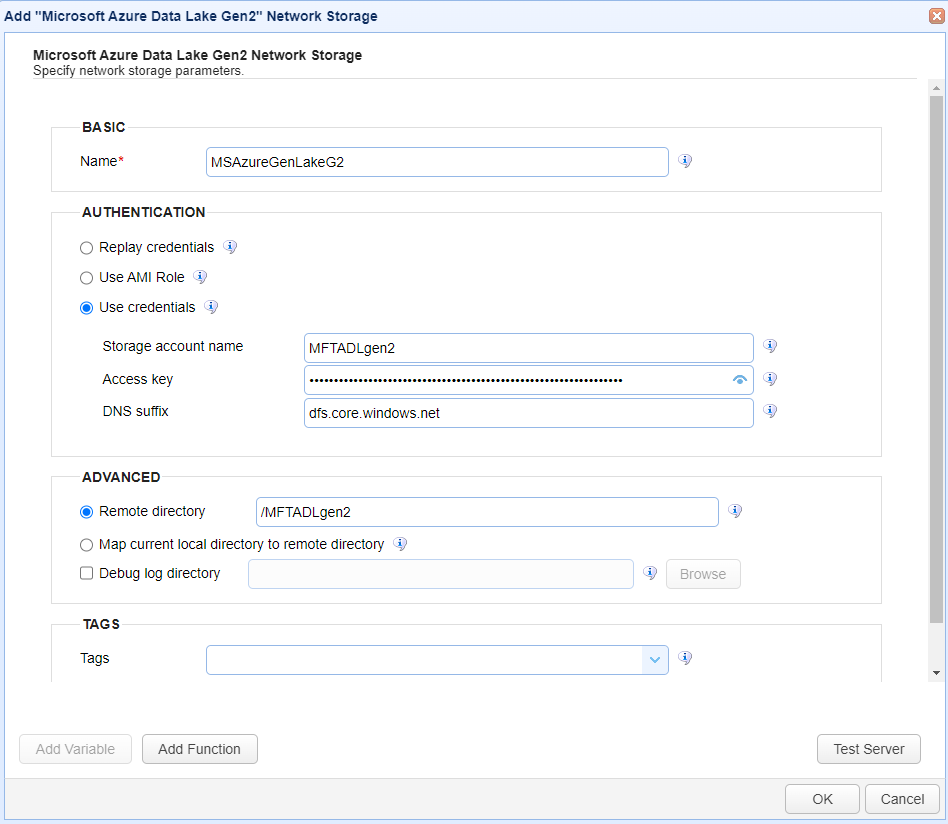
Below is a description of the Azure Data Lake Gen2 Network Storage fields.
BASIC
Name — Identifies the unique Network Storage name.
AUTHENTICATION
Replay credentials — Uses the current user's credentials instead of a static Client ID and Client Secret.
Note: Replay credentials is not supported for users who connect to the MFT Server using SFTP with public key authentication. This option is set on the domain-level inACCOUNTS > Users > Users > Add/Edit > Require public key authentication for SFTP.
Use AMI role — If selected, the Azure Managed Identity role is used. Managed identities can be used to authenticate any Azure resource that supports AD authentication. See the following for more information. What are Managed Identities for Azure resources?
Use credentials — If selected, allows the administrator to specify a Storage account name and Access Key for all users.
-
Storage account name — Identifies the account name for the Azure Data Lake Gen2 Network Storage.
-
Access key — Identifies the access key for the Azure Data Lake Gen2 Network Storage.
-
DNS suffix — Identifies the DNS suffix for the Azure Data Lake Gen2 Network Storage.
ADVANCED
Remote directory — If selected, maps the local virtual path to a specific remote path on the target server.
Map current local directory to remote directory — If selected, maps the local virtual path to the remote path with the same name.
Debug log directory — If selected, identifies the directory where debug logs are stored.
TAGS
Tags — Identifies one or more Tags used to limit administrative access to the Network Storage.