Manager Service
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Manager Service consists of two tabs, Manager Service and Access, depicted in the image below.
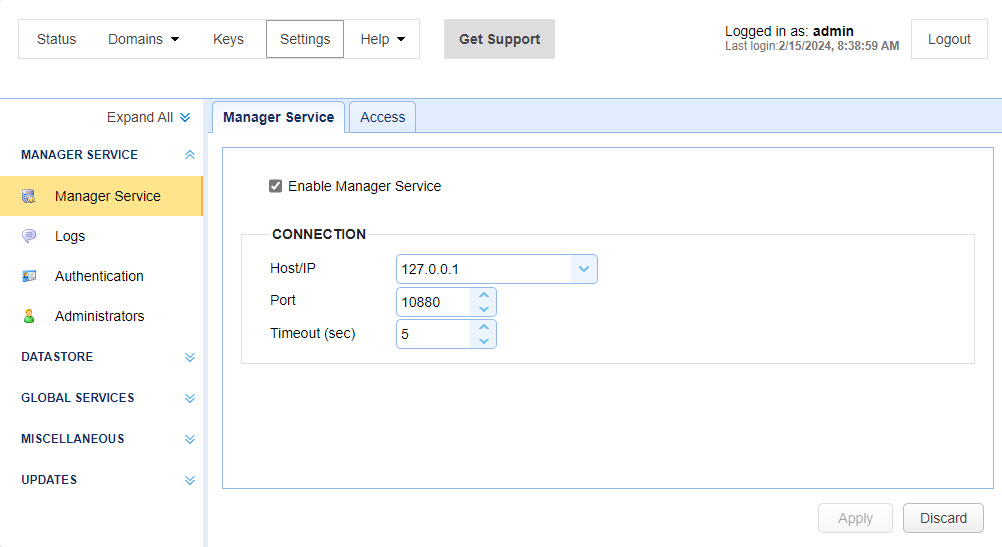
Manager Service

Enable Manager Connection - When checked, MFT Server will listen for Java API calls on the Host/IP and port specified. This allows for programmatic access to MFT Server configurations using the Java Management API. When unchecked, the system will not listen for incoming Java API calls.
Host/IP - The IP address that the MFT Server Service is running on.
Port - The port that the MFT Server Service is running on.
Timeout - Manager timeout in seconds when communicating with MFT Server Service.
Access
Administrative access may be restricted by client IP. This is recommended in high security environments where administrators may connect only from known client IP addresses. By default, MFT Server allows administrators to connect from ANY client IP address, but as an improved security measure you may define what IP addresses are allowed or denied access to the administrative service.
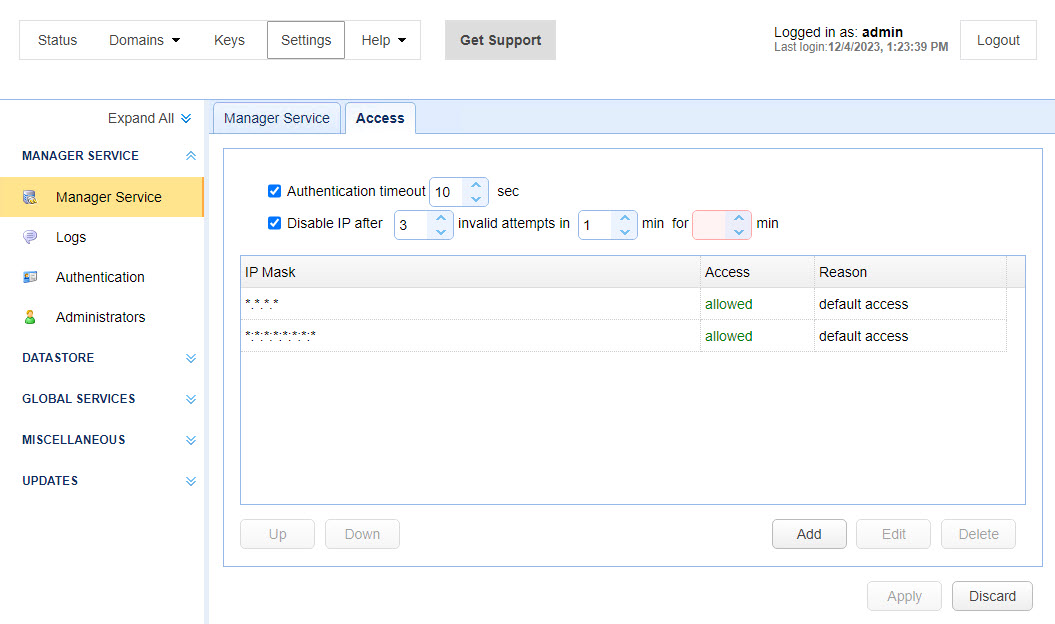
Authentication timeout - The amount of time in seconds that the administrative service client may remain connected without authenticating.
Disable IP after - Disables a client IP address after X invalid authentication attempts within Y minutes for Z minutes. See the Note below.
Note: When you allow specific IP address(s), and the "Disable IP after" option is enabled, the allowed IP(s) will not be disabled if too many invalid attempts occur, because they will bypass the Disable rule. The allowed IP(s) take precedence over the rule. In this scenario, you will still see a record in the Access grid stating there were too many invalid authentication attempts, but no action will be taken to block the IP. Always make sure any allowed IP's are trusted.
Access rules are processed in the order listed. For each connection, the first matching access rule will be used. Therefore, it is important that the access rules be ordered correctly to prevent an Admin from being mistakenly denied or granted access. You may use the
UpandDownbuttons to order the access rules to suit your needs.
If you are adding a deny rule - whether it is in CIDR notation, wildcard mask, fully qualified domain name (FQDN), or individual IP, please make sure to place (bring up) the rule to the top.
Examples of valid IP masks are as follows:
192.168.1.1 - Allows/Blocks a single IP address
192.168.1.* - Allows/Blocks all IP addresses in a class C IP block.
192.168.*.* - Allows/Blocks all IP addresses in a class B IP block.
*.*.*.* - Allows/Blocks all IP addresses.
*.domain.com - Allows/Blocks all host addresses associated with the specified domain name.
Host.domain.com - Allows/Blocks the host address on the specified domain.