Setting IP based access

As an improved security measure you may define what IP addresses are allowed or disallowed access to your domain services. To view a list of IP access rules click on the SECURITY > IP Access module for the desired domain.
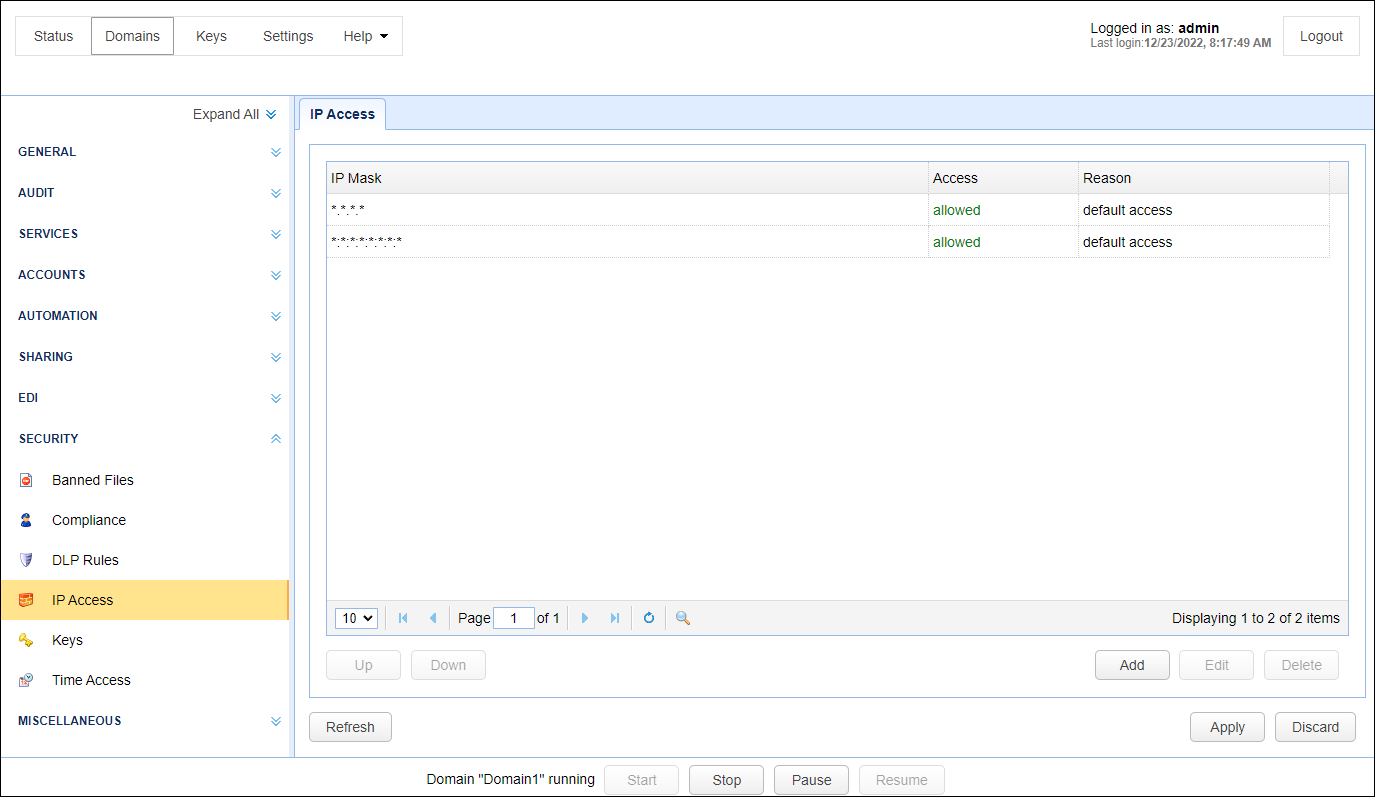
IP Mask - The IP address mask. Both wildcard (e.g. 192.168.1.*) and CIDR (e.g. 192.168.1.0/24) notations are supported. In addition, you can also use a FQDN in the mask field (e.g. my.domain.com, *.domain.com, or my.domain.*).
Access - Indicates whether access is allowed or denied.
Reason - The reason access is allowed or denied.
Access rules are processed in the order listed. For each connection the first matching access rule will be used. Therefore it is important that the access rules be ordered correctly to prevent a user from being mistakenly denied or granted access. You may use the Up and Down buttons to order these access rules to suit your needs.
If you are adding a deny rule - whether it is in CIDR notation, wildcard mask, fully qualified domain name (FQDN), or individual IP, please make sure to place (bring up) the rule to the top.
To add an access rule click on the Add button in the lower right corner. This will display the Add IP Access Rule dialog.
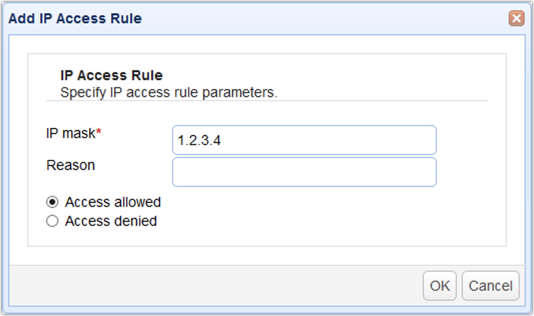
IP mask - The IP address or IP address mask to allow or deny access. Both wildcard (e.g. 192.168.1.*) and CIDR (e.g. 192.168.1.0/24) notations are supported. In addition, you can also use a FQDN in the mask field (e.g. *.domain.com or host.domain.com).
Reason - Reason access is allowed or denied.
Access allowed - Select to have access allowed. See note below.
Access denied - Select to have access denied.
Note:
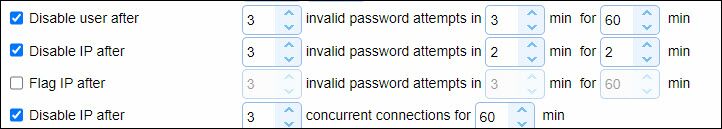
As per features discussed in the Setting connection preferences section, you can disable a user or IP address under certain circumstances (see the image below). When access is allowed for an IP address, and a rule has been established to disable IPs and/or disable users, and the disabling event occurs, the allowed IP or the user matching the allowed IP will not be disabled, because the allowed IP's are designed to bypass the disable rules. To summarize, the allowed IP(s) added in this module take precedence over the disable rules set in the SERVICES > Connections module. Should a disable event occur that is associated with an allowed IP, you will still see a record in the IP access grid that states the event happened (e.g. there were too many invalid authentication attempts), but as stated, no disabling will occur. Always make sure any allowed IP's are trusted.
The "Disable" rules that are bypassed for allowed IPs (should the disabling event occur) are checked in the image below. The image is taken from the SERVICES > Connections module.
Examples of valid IP masks are as follows:
-
192.168.1.1- Allows/Blocks a single IP address -
192.168.1.*- Allows/Blocks all IP addresses in a class C IP block. -
192.168.*.*- Allows/Blocks all IP addresses in a class B IP block. -
1
0.0.0.0/27- Allows/Blocks all IP addresses from 10.0.0.1 to 10.0.0.30 -
192.168.0.0/17- Allows/Blocks all IP addresses from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.127.254 -
*.*.*.*- Allows/Blocks all IP addresses. -
*.domain.com - Allows/Blocks all host addresses associated with the specified domain name.
-
Host.domain.com - Allows/Blocks the host address on the specified domain.