Microsoft Azure Data Lake network storage
The Microsoft Azure Data Lake network storage option allows you to use existing Microsoft Azure Data Lake storage as additional storage space.
Adding the Microsoft Data Lake network storage
In the desired domain, navigate to the ACCOUNTS > Network Storage module. Click on the Add button, or right click anywhere in the grid area and select Add from the pop-up menu. In the Add Network Storage dialog window, select Microsoft Azure Data Lake as the Protocol, then click on OK. The Add "Microsoft Azure Data Lake" Network Storage dialog will appear as depicted in the image below.
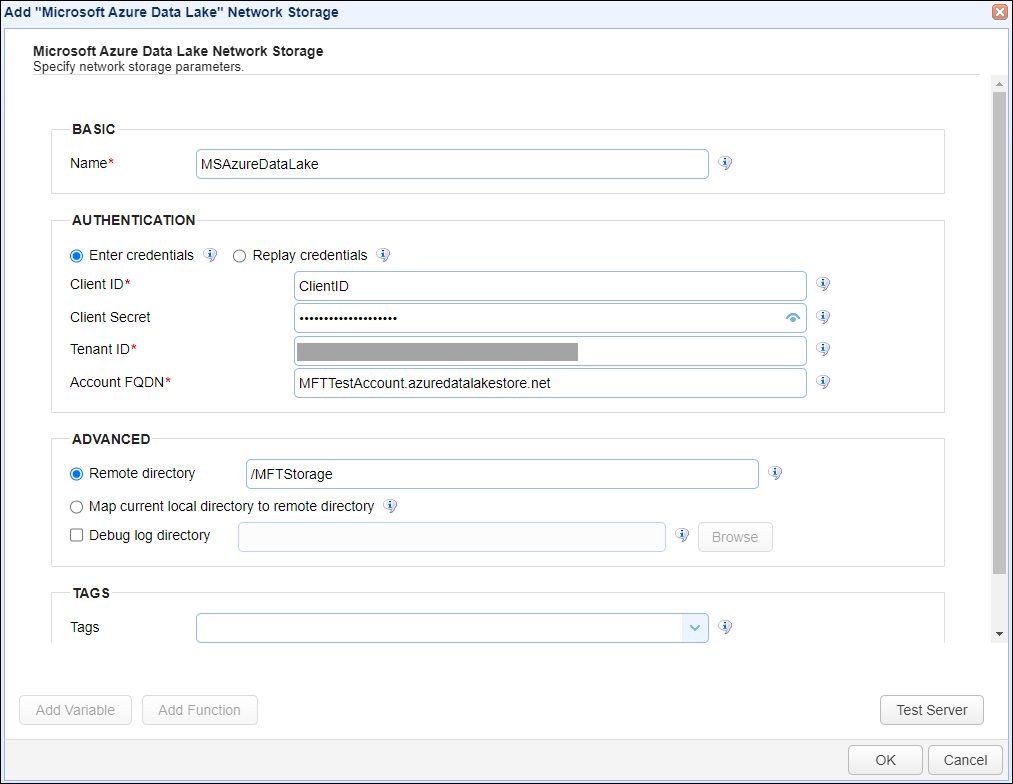
Basic
Name - The unique name for this network storage.
Authentication
Enter credentials - If selected, allows the administrator to specify a Client ID and Client Secret for all users.
| · | Client ID - The client ID for the Azure Data Lake network storage. |
| · | Client Secret - The client secret for the Azure Data Lake network storage. |
Replay credentials - If selected, uses the current user's credentials instead of a static Client ID and Client Secret. Note: This feature will not work for users who authenticate to the SFTP service via public key authentication.
Tenant ID - The tenant ID for the Azure Data Lake network storage.
Account FQDN - The fully qualified domain name.
Advanced
Remote directory - If selected, maps the local virtual path to a specific remote path on the target server.
Map current local directory to remote directory - If selected, maps the local virtual path to remote path having the same name as the local virtual path. For example, if network storage is mapped to virtual path /path, then when connecting to the network storage, it will drop the user in /path directory on target server.
Debug log directory - If checked, this is the directory where debug logs will be stored for this network storage.
Tags
Tags - If specified, this is the one or more tags that are used to limit which administrators have access to the network storage.