Authenticating using custom authentication API
The custom authentication API provides you with a way to authenticate users using your own business rules. The custom authentication API is recommended when the other built-in authentication modules (Database, LDAP, Domain) do not meet your needs. To implement your own authentication provider you must perform the following:
-
Create a class which implements the
com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.AuthenticationServiceclass. -
Overload the
public void authenticate(Credentials creds)method, throwing acom.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.AuthenticationException exceptionif authentication fails. -
Create a JAR file that contains the compiled version of your
com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.AuthenticationServiceimplementation. To compile your authentication class you will need to include the ftpserver.jar library in your classpath. The ftpserver.jar library may be found in thelibsdirectory for MFT Server. -
Place the JAR file created in Step 3 as well as any needed 3rd party JAR files into the
libs/extdirectory of your MFT Server installation. -
Restart the MFT Server Service.
-
Open MFT Server Manager and select the
ACCOUNTS > Authentication > Authenticationtab. -
Change
Service typetocustom authentication. Type in the class name created in Step 1 into theAuthentication classfield.
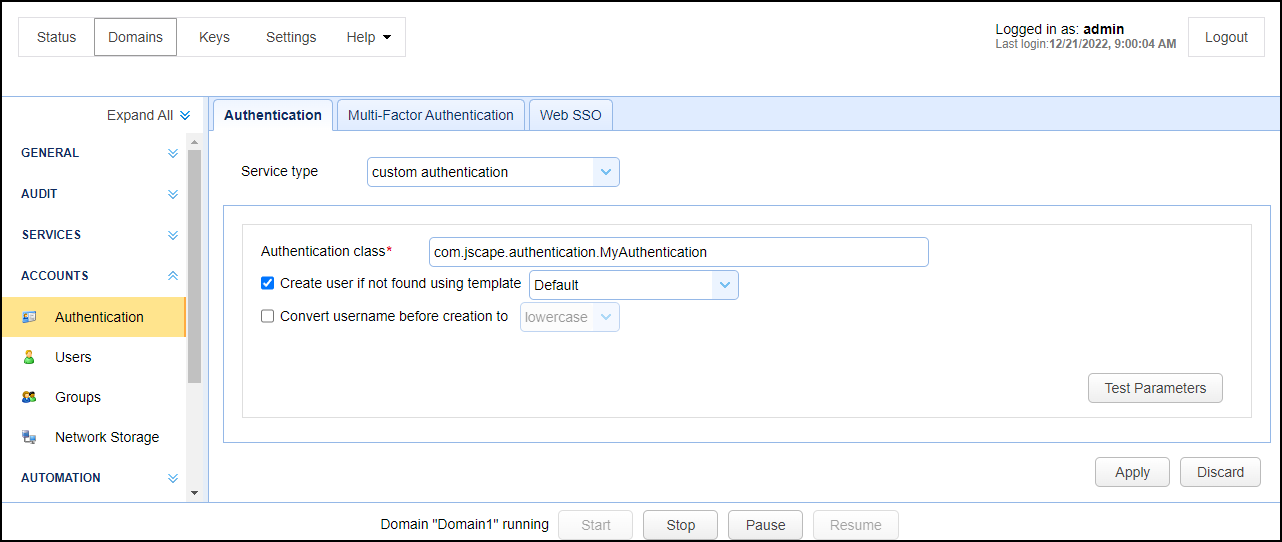
Authentication class - The custom authentication class name.
Create user if not found using template - This allows for accounts to be created automatically upon successful authentication. If selected, an account will be created automatically (if it does not exist already) using the specified User Template.
Convert username before creation to - If enabled, the username supplied will be converted to specified case before passing username to specified User Template.
Example
package test.jscape;
import com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.AuthenticationException;
import com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.Credentials;
import com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.authentication.AuthenticationService;
/**
*Example class to implement IP/user based authentication
*/
public class UserIPAuthentication implements AuthenticationService {
private static final String username = "jsmith";
private static final String password = "secret";
private static final String ip = "127.0.0.1";
/**
*Authenticate user credentials
*/
public void authenticate(Credentials creds) throws AuthenticationException {
if(creds.getLogin().equals(username) && creds.getPassword().equals(password)
&& creds.getClientIp().equals(ip)) {
// ignore
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("Authentication failed: " + creds.getLogin() +
":" + creds.getClientIp() + ":" + creds.getPassword());
}
}
}
The example above authenticates successfully if the username is "jsmith", the password is "secret" and the client IP address is "127.0.0.1".
See also
Setting authentication preferences