Microsoft OneDrive/SharePoint network storage
The Microsoft OneDrive/SharePoint network storage option allows you to use existing Microsoft OneDrive or SharePoint storage as additional storage space.
Adding the Microsoft OneDrive/SharePoint network storage
In the desired domain, navigate to the ACCOUNTS > Network Storage module. Click on the Add button, or right click anywhere in the grid area and select Add from the pop-up menu. In the Add Network Storage dialog window, select Microsoft OneDrive/SharePoint as the Protocol, then click on OK. The Add "Microsoft OneDrive/SharePoint" Network Storage dialog will appear as depicted in the image below.
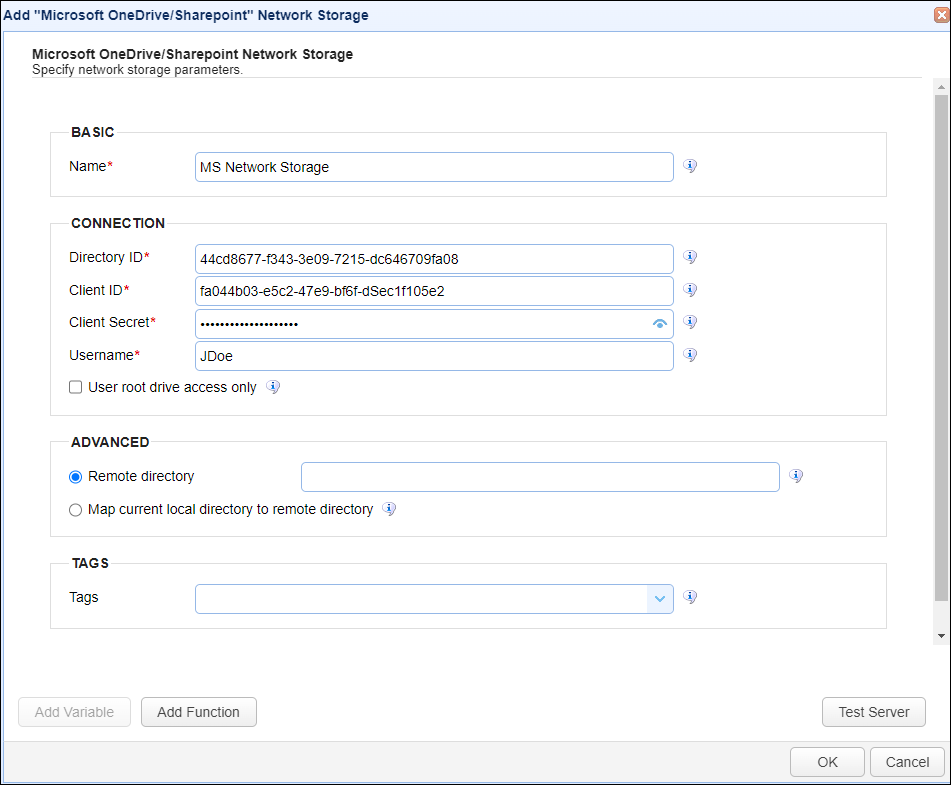
Basic
Name - The unique name for this network storage.
Connection
Directory ID - The directory ID for the Microsoft OneDrive network storage.
Client ID - The client ID for the Microsoft OneDrive network storage.
Client Secret - The client secret for the Microsoft OneDrive network storage.
Note: The Directory ID, Client ID and Client Secret are obtained using the Azure portal. Log in, navigate to the registered application (a process the Azure admin must complete to allow MFT Server access to the Azure API ), select the left-side menu option Overview, then copy the Directory (tenant) ID and Application (client) ID. For the client secret, select the left-side menu option Certificates & Secrets, then copy the client secret.
Username - The username for the connecting to the remove server.
Use root drive access only - When checked, access will be limited to the user's default drive (the root drive, named OneDrive). Leave this box unchecked so that access to users and their associated drives can be obtained through SharePoint site(s). Please note that the registered application's API Permissions (another left-side menu option in the Azure portal) determines OneDrive/Site access. See below.
-
For reading/writing site files (Site access) - Sites.ReadWrite.All
-
For reading/writing files (OneDrive access) - Files.ReadWrite.All
Advanced
Remote directory - If selected, maps the local virtual path to a specific remote path on the target server.
Map current local directory to remote directory - If selected, maps the local virtual path to remote path having the same name as the local virtual path. For example, if network storage is mapped to virtual path /path, then when connecting to the network storage, it will drop the user in /path directory on target server.
Tags
Tags - If specified, this is the one or more tags that are used to limit which administrators have access to the network storage.