Health Monitor
Health Monitor is a feature that is typically used when running multiple MFT Server instances in an Active/Active high availability (HA) environment. The Health Monitor Action finds the first available MFT Server instance, and sets a global variable identifying the system. The variable value is the MFT Server's unique Instance ID.
A use case for this Action is as follows: Assume you have one or more Triggers configured using the Trigger Event type Current Time. This type of Trigger runs (by default) on all active MFT Server instances in an HA environment. Assume you want to limit the execution to one MFT Server instance. You can accomplish this using the Health Monitor Action.
The Health Monitor Action takes a list of MFT Servers (that you provide) and iterates through it, performing a TCP socket connection test to the host's specified port. This quickly determines if the MFT Server service on that host is up and listening. The moment a host successfully passes the connection test, the Health Monitor Action stops checking the rest of the systems in the list. MFT Server then sets a global MFT Server variable (whose name is configured in the Action) to the unique Instance ID of the available MFT Server instance.
Next, for any Current Time Triggers, you can set a Trigger Condition to only run the trigger if the Instance ID of the MFT Server instance matches the global variable set by the Health Monitor Action.
The Health Monitor Action is typically run in a separate, stand-alone Trigger, on a schedule using Current Time. For example, you can set the time so that the Trigger runs every 10 minutes. This means the MFT Server will check the list of MFT Server instances every 10 minutes, and update the global variable with the first system on the list that successfully passes the connection test. If something should unexpectedly occur with an MFT Server instance (making it unavailable), the variable will be updated to reflect a system that is available.
AUTOMATION > Triggers > Settings. If the variable is not present the first time the Health Monitor Action runs, it is automatically created, and you will see it in the above described location.
The global variable that is assigned the Instance ID of an available MFT Server is then used in a Trigger Condition, for any Current Time event type Trigger. The Instance ID of the MFT Server instance must match the value of the global variable. Since the Instance ID is unique, the condition will only evaluate to true on one MFT server in the HA configuration.
The Trigger Condition will look this: ApplicationInstanceId = GetGlobalVariable("Trigger_Executor"), where Trigger_Executor is the configurable global variable name. You must manually enter the Condition Expression (enable Override Expression) because the expression contains a function, which is not supported when using the expression builder option.
See below the images that depict what is described above.
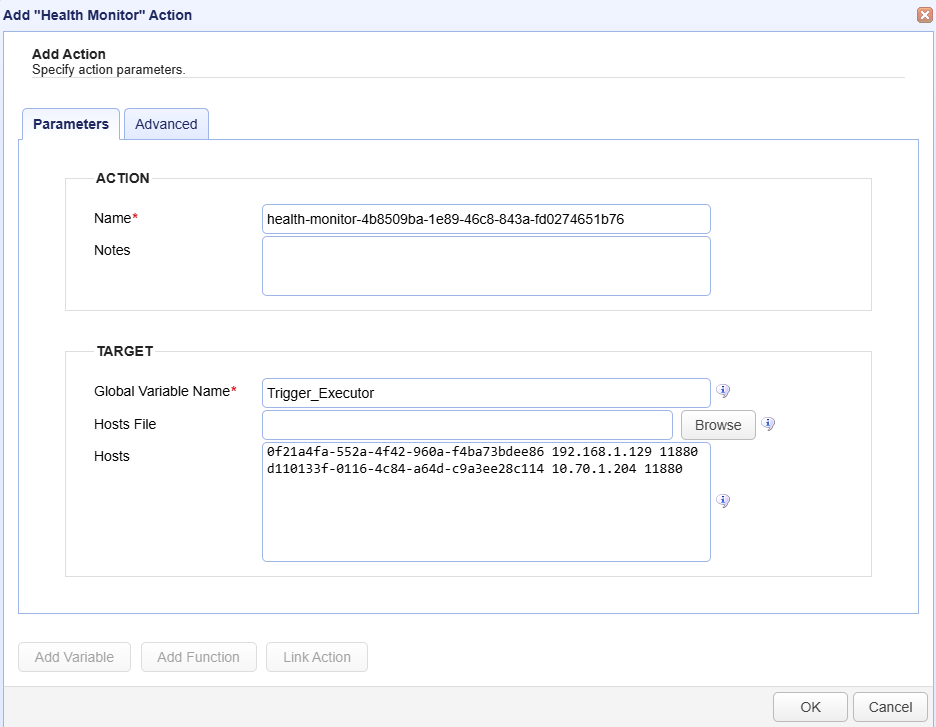
Parameters tab
ACTION
Name — Identifies the name of the Action. The system-generated default name, depicted in the image above, can be changed to a different name to suit your preferences. The Name must be unique within the current Trigger workflow.
Notes — Describes the Action.
The values in the Name and Notes fields are displayed in a tooltip when you mouse over an Action node.
TARGET
Global Variable Name — Identifies the name of the variable. You can assign it a name to suit your preference.
Hosts File — Identifies the file where the list of MFT Server instance information is stored. Alternatively, you can enter the MFT Server instance information directly in the Hosts field. Choose the option you prefer.
Hosts — Identifies the MFT Server instance information.
If the Hosts File cannot be found (or the field is blank), or if it is found but a connection to an MFT Server is unsuccessful, the system will check the Hosts field (if information has been provided) and iterate through that list.
For the Host File and Hosts fields, the information entered is the same, using the format described below.
Instance ID <space> IP Address <space> Port — one line per instance.
9c8c66df-3c80-492f-8c72-b341f2156bdb 10.70.1.204 11880
To locate the MFT Server's Instance ID, navigate to
Status > Server > Instance ID(copy it from this location).
Set the port number to a port that is always available on the MFT Server instance, such as the MFT Server REST port, which by default is 11880. See
Settings > MISCELLANEOUS > Web > RESTto confirm your REST port number.
Obtain the MFT Server's IP address using the appropriate operating system-specific command.
The Trigger that includes the Health Monitor Trigger Action should be configured with the
Current TimeEvent type (set in the Trigger's Parameters tab). To run the Trigger every 10 minutes (as an example), set the Trigger Condition to:Minute = 0 OR Minute = 10 OR Minute = 20 OR Minute = 30 OR Minute = 40 OR Minute = 50.
Now that the Health Monitor Trigger is complete, it's time to apply the Trigger Condition expression to the one or more Triggers that are configured using the Current Time Event type. The condition would look similar to what is displayed below - ApplicationInstanceId = GetGlobalVariable("Trigger_Executor").
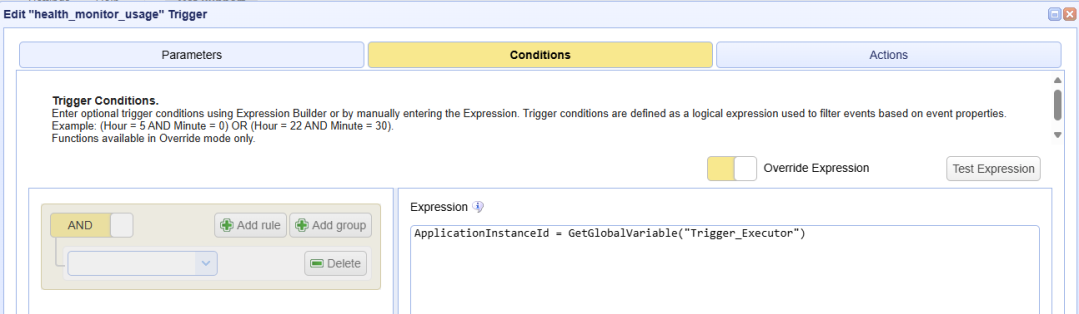
It is not unusual to have a Current Time Trigger configured with a Condition specifying the time(s) the Trigger should run (if you do not want it to run every minute, the default behavior). In this case, the Condition would look similar to the image displayed below (in this example, the Trigger runs once a day at 4:45 PM).
Advanced Tab
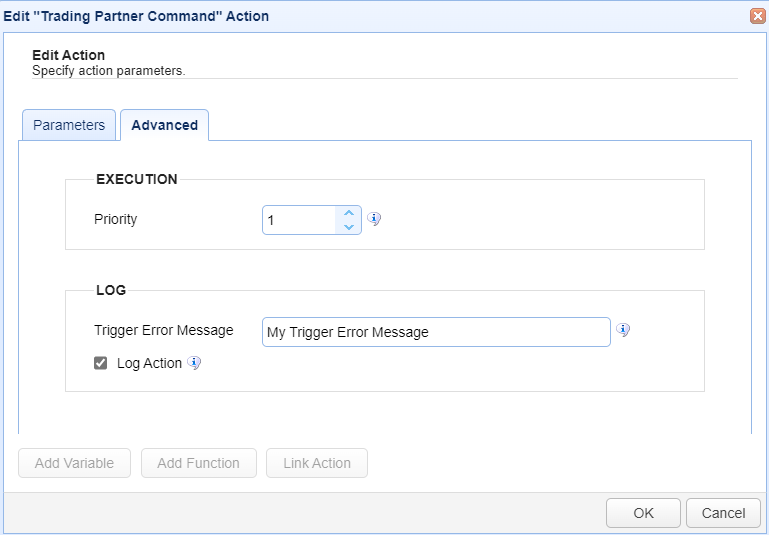
EXECUTION
Priority — Identifies the Action’s priority. An Action can be interrupted by an Action with a higher priority. The highest priority is 1. The maximum priority value is 1000. Priority comes into play when certain scenarios occur, like when Triggers or transfers are exceeded (see Settings for more information).
LOG
Trigger Error Message — Used when a Trigger Action fails. The two uses are described below.
The Trigger Error Message is displayed in the
Trigger Errorcolumn of the Action history (Triggers > History > View).
If you create an error-handling Trigger, the Trigger Error Message is passed to the error-handling Trigger.
An error-handling Trigger is a distinct Trigger that uses the
Trigger ErrorEvent type, as selected in theTrigger > Parametersdialog.If a Trigger Error event occurs, the Trigger Error Trigger runs.
The Trigger Error Message is accessible in the Trigger Error Trigger as a variable named TriggerErrorMessage.
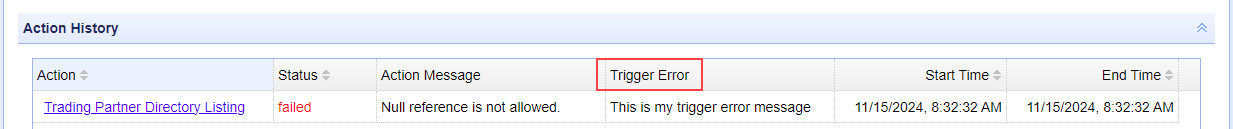
The image below depicts the
Trigger Error Messagedisplayed in the history of a failed Trigger Action.
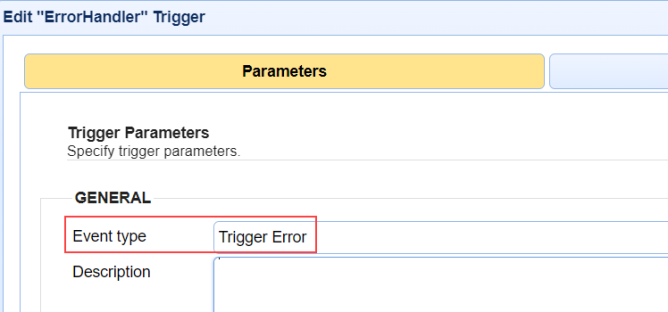
The image below depicts selecting the
Trigger ErrorEvent type used to handle Trigger errors.
The image below depicts a Trigger Action (part of the Trigger Error Trigger workflow) accessing a
Trigger Error Message. This is accomplished using the TriggerErrorMessage variable. To reference built-in variables, enclose the variable name in percent signs (%).

As a practical use case example, you can reference the
Trigger Error Messagein the body of an Email Action that is part of the Trigger Error workflow. The email alerts interested parties that a Trigger Action failed.Log Action — When selected, Trigger Action records are added to the
Domain > AUDIT > Loggingmodule. The state of the Action is included, such as action started, action completed, and action failed. When unselected, Action records are not added to the Logging module. However, the Trigger itself is still logged.
Buttons
Add Variable— Displays a list of built-in event variables. Each Trigger has several event variables you can use in one or more of the Trigger Action fields. When a variable is selected from the list, it is added to the Action field that is currently active. Built-in event variables are enclosed using the percent sign (e.g., %DomainName%).
In addition to using built-in variables, you can also specify a user-defined global variable, created in
AUTOMATION > Triggers > Settings. To reference a global variable ( Defining global variables), use the %GetGlobalVariable% function.
%GetGlobalVariable("DirName")% retrieves the global variable named DirName. When using global variables, specify the variable name enclosed in quotes, as depicted in this example.
Add Function— Displays a list of built-in functions. Functions are useful for formatting or parsing a Trigger event variable. When a function is selected from the list, it is added to the Action field that is currently active. For more details about functions and their usage, see Function types.
Link Action— Displays a list of Actions. When an Action is selected, the Action ID is returned.
An Action ID (a string of alphanumeric characters) is an input parameter used in the
GetActionResultfunction. This function returns the results of a previously executed Action in the current Trigger workflow. This means that Action results can be passed to a linked (following) Action.
TheGetActionResultfunction also supports using the ActionNameas an input parameter. This is an enhancement added in a more current version of MFT Server.Using Link Action
Select a field in the Trigger Action that you want to populate using the results of a previous Action.
Click Add Function. A list of functions displays.
Select GetActionResult(actionId). The field displays %GetActionResult(actionId)%.
Highlight the word
actionIdin the field.
Click Link Action. A list of Actions displays.
Select an Action. The actionId text is replaced with the Action ID.
The GetActionResult function looks similar to this: %GetActionResult("bee7cd8b-8021-4e19-8f76-1ae382e60c9d")%