Amazon S3 network storage
This Network Storage uses Amazon S3 Cloud object storage as additional storage space.
Adding the Amazon S3 Network Storage
In the desired domain, navigate to the ACCOUNTS > Network Storage module. Click Add. The Add Network Storage dialog displays. Select Amazon S3 as the Protocol, then click OK. The Add "Amazon S3" Network Storage dialog displays as shown below.
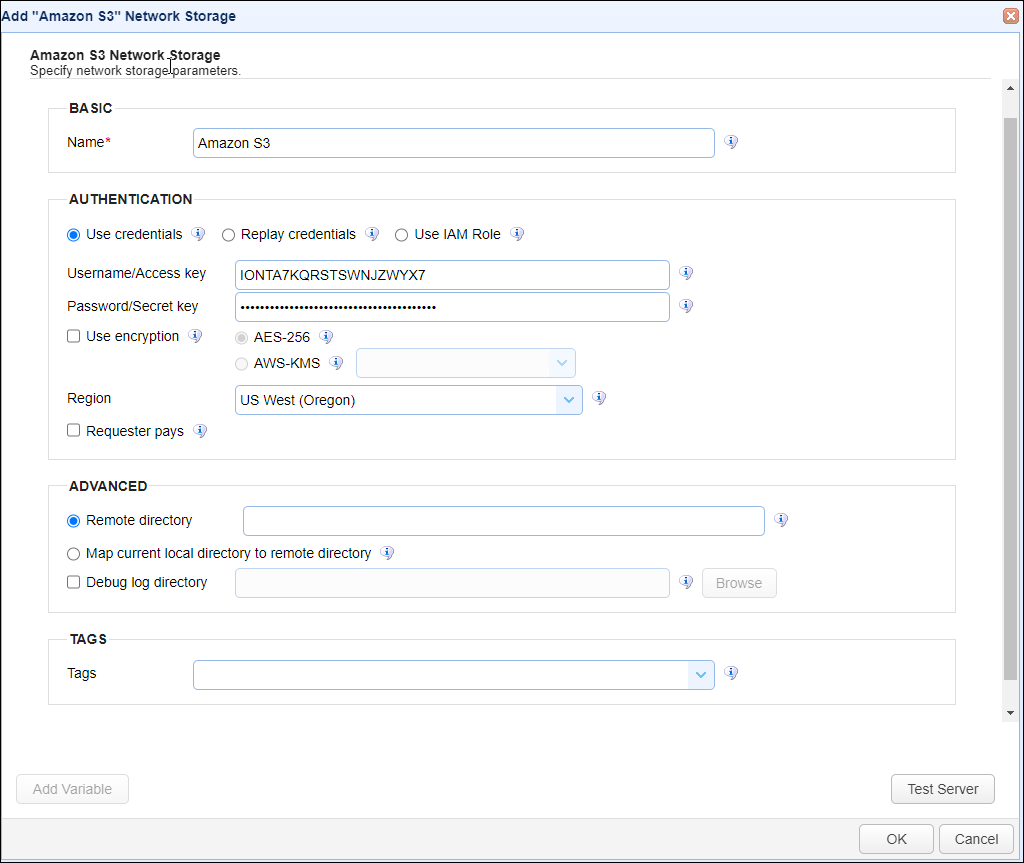
Below is a description of the Amazon S3 Network Storage fields.
BASIC
Name — Identifies the unique Network Storage name.
AUTHENTICATION
Use Credentials — If selected, the Username/Access key and Password/Secret Key fields are used to authenticate access to the Amazon S3 Storage.
-
Username/Access key — Identifies the User name/Access key
-
Password/Secret key — Identifies the Password/Secret key
Replay credentials — If selected, uses the current user's credentials to authenticate the Amazon S3 Storage instead of a static Username/Access key and Password/Secret key.
ACCOUNTS > Users > Users > Add/Edit > Require public key authentication for SFTP.
Use IAM Role — If selected, uses the Identity and Access Management role for authentication.
When connecting to an Amazon S3 Trading Partner and/or Network Storage using the IAM Role, it assumes the role provided by the EC2 metadata. While this works for most instances, it does not work when using a Kubernetes cluster. Therefore, below you will find instructions how to access an AWS S3 Bucket from a K8 Cluster using the IAM role feature.
Create an IAM role with the following policy document. Replace jscape-test-eks-bucket with your bucket name.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:PutObjectAcl"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::jscape-test-eks-bucket",
"arn:aws:s3:::jscape-test-eks-bucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Attach the IAM role to the cluster's node or instance.
Create a JSCAPE MFT pod using the Docker Instructions below:
Note: Modify the Policy document if the MFT needs to access more S3 buckets.
Use encryption — If selected, enables encryption for the Network Storage. Choose AES-256 or AWS-KMS server-side encryption.
-
AES-256 uses Amazon S3 managed keys.
-
AWS-KMS uses AWS KMS managed keys.
-
AWS-KMS keys are created in AWS via the Key Management Service. The dropdown for this field pulls in a list of available keys from AWS.
-
Region — Identifies the Amazon region where the S3 bucket resides.
Requester pays Debug log directory — If selected, specifies the directory where debug logs are placed for this Network Storage. If selected, the Amazon S3 bucket is a requester pays bucket, meaning the requester pays the cost of the request and data download instead of the bucket owner.
Policy 1
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::the-bucket"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:DeleteObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::the-bucket/*"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor2",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Policy 2
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::the-bucket"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:DeleteObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::the-bucket/*"
}
]
}
ADVANCED
Remote directory — If selected, maps the local virtual path to a specific remote path on the target server.
Map current local directory to remote directory — If selected, maps the local virtual path to the remote path that has the same name as the local virtual path.
Debug log directory — If selected, specifies the directory where debug logs are stored.
TAGS
Tags — Identifies one or more Tags used to limit administrative access to the Network Storage.