AFTP Network storage

Accelerated File Transfer Protocol (AFTP) Network Storage lets you use a remote system as additional storage, provided it is configured with AFTP.
AFTP is protocol developed by JSCAPE. It runs on top of the UDP protocol and provides fast file transfers over networks that experience high latency and packet loss. Since AFTP is developed by JSCAPE, the Network Storage discussed here refers to another instance of MFT Server with the AFTP service configured.
Adding the AFTP Network Storage
In the desired domain, navigate to the ACCOUNTS > Network Storage module, then click Add. The Add Network Storage dialog displays. Select AFTP as the Protocol, then click OK. The Add "AFTP" Network Storage dialog displays as shown below.
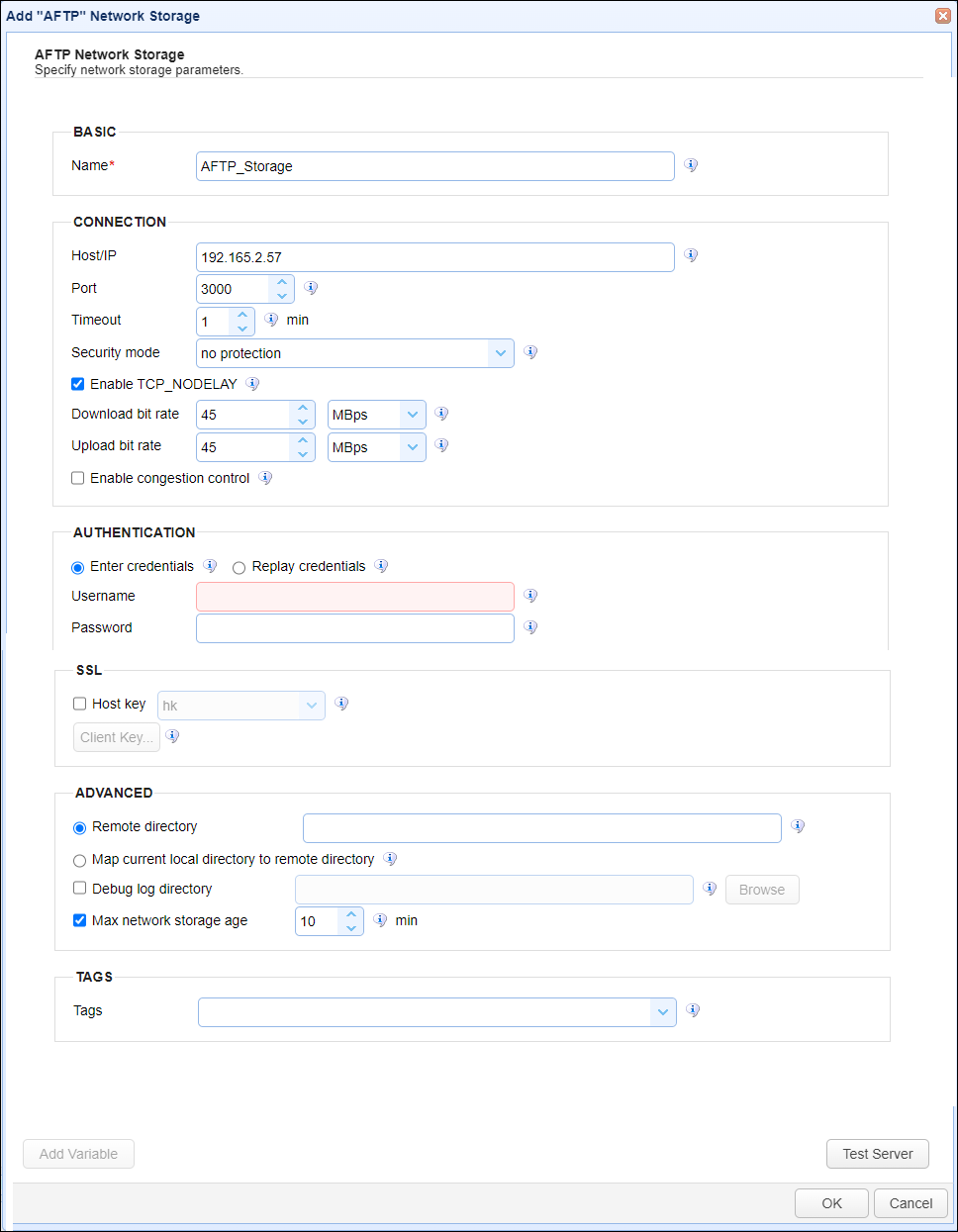
Below is a description of the AFTP Network Storage fields.
BASIC
Name — Identifies the unique Network Storage name.
CONNECTION
Host/IP — Identifies the remote MFT Server hostname or IP address.
Port — Identifies the port for used to communicate with the remote MFT Server.
Timeout — Identifies the maximum timeout (in minutes) for establishing a connection to remote MFT Server.
Security Mode — Identifies the security mode. Options include no protection, authentication and data protected, and authentication protected.
Enable TCP_NODELAY — If checked, Nagle's algorithm is disabled.
Download bit rate — Identifies the download bit rate in KBps,MBps, or GBps.
Upload bit rate — Identifies the upload bit rate, in KBps, MBps, or GBps.
Enable congestion control — If selected, congestion control is enabled.
AUTHENTICATION
Enter credentials — If selected, a static Username and Password are used for all Users that have access to this Network Storage.
Username — Identifies the user name that connects to the remote server. This is a User created on the remote MFT Server in the [Domain] >
ACCOUNTS > Usersmodule.Password — Identifies the password for the above Username field.
Replay credentials — If selected, uses the current user's credentials instead of a static Username and Password. This means the current user is defined on the remote MFT Server in the Domain > ACCOUNTS > Users module.
Replay credentials is not supported for users who connect to the MFT Server using SFTP with public key authentication. This option is set on the domain-level inACCOUNTS > Users > Users > Add/Edit > Require public key authentication for SFTP.
SSL
Host Key — If selected, it is the key used to verify the identity of the remote MFT Server where AFTP is configured. The field's dropdown list lets you to select a Host Key that is managed by the Key Manager.
Client Key — If selected, specifies the client key type used when authenticating with the remote MFT Server where AFTP is configured.
The Security Mode field described above must be set toauthentication and data protected, orauthentication protectedfor the Client Key field to be enabled.
Use one-time key — Identifies the one time key.
User server key — Identifies the server key, where you select from a list of existing server keys managed by the Key Manager.
Use key file — Identifies the file-based key.
Key file password — Identifies the optional key file password to be used for the connection.
ADVANCED
The options here determine the physical path on the remote system that the connecting user's virtual path maps to. As a reminder, the Network Storage virtual path name is configured on the user-level (ACCOUNTS > Users > Users (User name) > Paths > Path) or on the group-level (ACCOUNTS > Groups > (Group name) > Paths > Path) where the user is a member.
Remote directory
If selected, the value entered here is the physical path (in part) on the remote MFT Server system the connecting user's virtual path is mapped to. It is the path they are placed in when accessing the Network Storage. To be precise, the Remote directory is added as a subdirectory to the authenticating user's root path, on the remote MFT Server system.
C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe, and the Remote Directory entered is: AFTPStorage. In this scenario, the connecting user is placed in the following directory when accessing the Network Storage's virtual path: C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe\AFTPStorage.
C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe.
Map current local directory to remote directory
If selected, the local user's virtual path name for this Network Storage is used (in part) to map to the physical path on the remote MFT Server system. The user's virtual path name is added as a child directory on the remote system, placed under the authenticating user's root path.
This means every user that has access to this AFTP Network Storage is placed in (have access to) the AFTP's physical path that includes (in part) their virtual path name. If the virtual path names for the AFTP Network Storage are unique for each user, then each user will have access to a physical directory on the MFT Server system that is specifically for their use. Alternatively, if a virtual path name is the same for multiple local users, those users have access to the same physical directory on the MFT Server system.
C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe. A connecting user's virtual path for this Network Storage is /User4Path. The connecting user is placed in this directory on the remote system: C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe\User4Path. If a different connecting users virtual path is /User5Path, they are placed in this directory on the remote system:C:\Program Files\MFT Server\Users\Domain1\JDoe\User5Path.
Add/Edit Virtual path dialog window has the Create directory if not found check box selected.
Debug log directory — If selected, specifies the directory where debug logs are stored.
C:\MFTServer\NetworkStorage\debug.
Max Network Storage age — If selected, identifies the maximum number of minutes to keep the Network storage connection in the connection pool.
TAGS
Tags — Identifies one or more Tags used to limit administrative access to the Network Storage.