Administrator Authentication
There are several authentication options you can choose from to secure Administrator (Admin) access to MFT Server. Administrators are the people who connect to your MFT Server to manage the system, like create Users, Groups, Trading Partners, etc. Administrator Authentication is configured in the Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Authentication > Authentication > Service module. Below are the authentication types to choose from.
LDAP Query Authentication (and its associated filters - LDAP Filter Grammar)
See also:
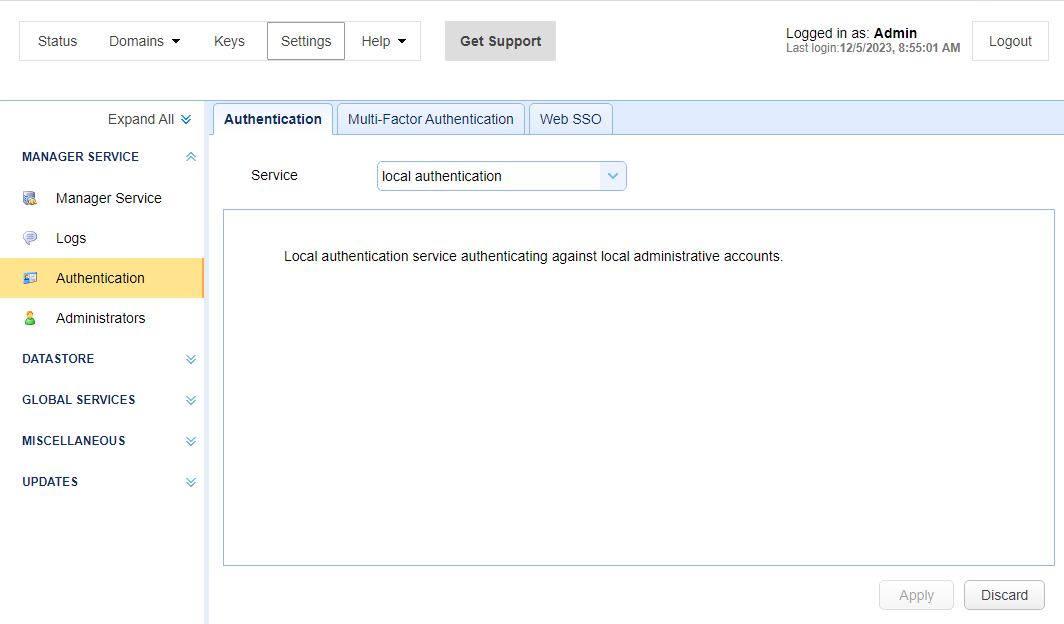
Local authentication is the most basic form of Administrator authentication. It authenticates Administrator accounts created and stored in MFT Server. See the image below, where the Service field is local authentication. When this authentication Service type is selected, each Administrator is authenticated using its assigned Login and Password. The Administrator accounts are created and modified in the Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administrators module.
If more than one Administrator is connecting to MFT Server, an existing MFT Server Administrator must create them in the Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administrators grid, then provide each Administrator with their user Login and Password. The password is stored encrypted in the MFT Server database.
General Information about non-local authentication services
For the remaining Service types (excluding local authentication) described below, authentication takes place using a service outside the realm of MFT Server. That said, there still must be a record for the Administrator in the MFT Server's Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administrators grid. This record is used for authorization purposes (the permissions associated with the Administrator). There are 2 ways to manage the creation of the Administrator record in the Administrators grid.
-
Create the Administrator (prior to the Administrator logging in) in
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administratorsgrid. TheSettings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administrators > Loginfield should be assigned the same login value (typically the user name) that is used to authenticate the Administrator for the selectedService.When using database authentication, if the Administrator logs in to the database with a name of JDoe, then that same name must be the value entered in theAdministrators > Loginfield.The
Loginfield is always unique. TheSettings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administrators > Passwordfield is not used, since authentication occurs using theServicetype configured. As mentioned earlier, the password is only used for thelocal authenticationService type. -
Let MFT Server create the Administrator in the
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administratorsgrid, during the login process, if a record for the Admin account does not exist. This feature is enabled by checking theSettings > MANAGER SERVICE > Authentication > Authentication > Create user if not found using <role>field. When this option is selected, the following occurs after the Admin successfully authenticates using the configuredServicetype:-
If a record does not exist in the
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administratorsgrid (theLoginfield is the search field used), then one is created for the Admin by MFT Server. The new Admin'sLoginfield is assigned the same value the Admin entered (user name) when authenticated using the selectedServicetype. A random system-generated password is assigned to the new Admin account. As stated in item 1, the password field is not used for authentication when an authentication method outside of MFT Server is used. Therefore, the value of the random password is irrelevant.
The<role>selected is important because the role's field settings are assigned to the new Admin account. This includes authorization for various global and domain settings. -
If a record does exist in the
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administratorsgrid (theLoginfield is the search field used), then the record is used for authorization purposes, and the login will be successful.
If the
Create user if not found using <role> fieldis not checked, and a matching record is not found in theSettings > MANAGER SERVICE > Administrators > Administratorsgrid (it was not manually created, as described in item 1), the login fails. The login also fails if the Admin does not authenticate using theServicetype selected.
Database authentication lets you authenticate an Administrator based on their rights to connect to a specific database. The user name and password entered when logging in to MFT Server are used to connect to the database identified in the JDBC URL. If the Administrator authenticates using the JDBC URL, then the Administrator is considered a valid MFT Server Administrator.
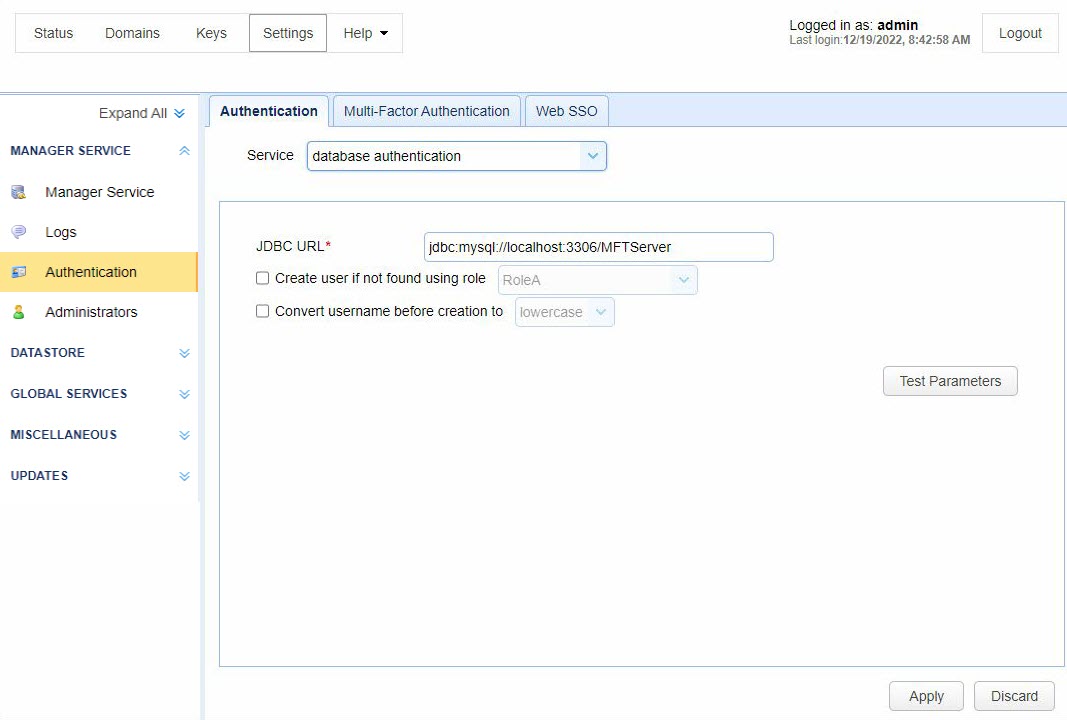
JDBC URL — Identifies the JDBC URL used to connect to the database. Libraries for JDBC drivers must be placed in the libs/jdbc directory of your MFT Server installation, and the MFT Server service must be restarted for the database to be accessible to MFT Server.
Create user if not found using role — If selected, and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the username supplied is converted to the lower or uppercase before creation.
Database Query authentication lets you authenticate an Administrator based on the results of a database query. If one or more records are returned from the query, then the Administrator successfully authenticates.
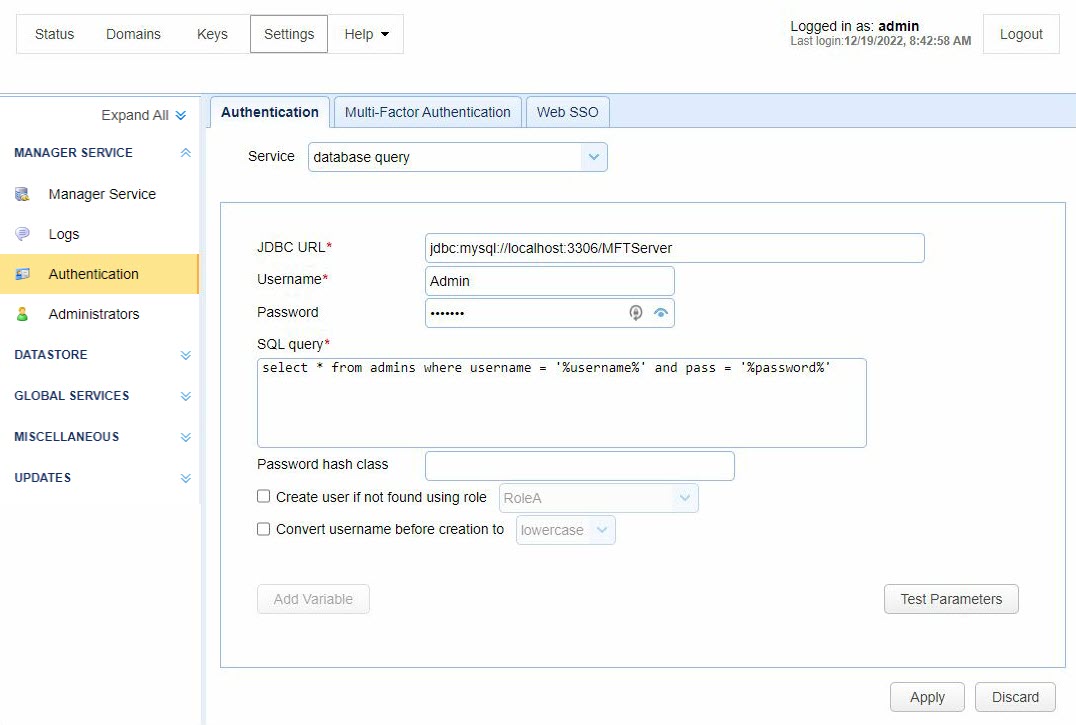
JDBC URL — Identifies the JDBC URL used to connect to the database. Libraries for JDBC drivers must be placed in the libs/jdbc directory of your MFT Server installation. Additionally, the MFT Server Service must be restarted to allow the database to be accessible to MFT Server.
Username — Identifies the username to connect with when authenticating using a JDBC database.
Password — Identifies the password to connect with when authenticating using a JDBC database.
SQL query — Identifies the query to execute when authenticating the Admin. There are two special variables that may be used when performing the database query %username% and %password%. They refer to the username and password passed in during the authentication process.
Password hash class — Identifies the Java class to use for password hashing before passing it to the SQL query. The password is passed to the SQL query in clear text if no class is specified.
Create user if not found using role — If selected and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the username supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the SQL query and the Role.
LDAP authentication lets you authenticate an Administrator based on their ability to connect to an LDAP or Active Directory service.
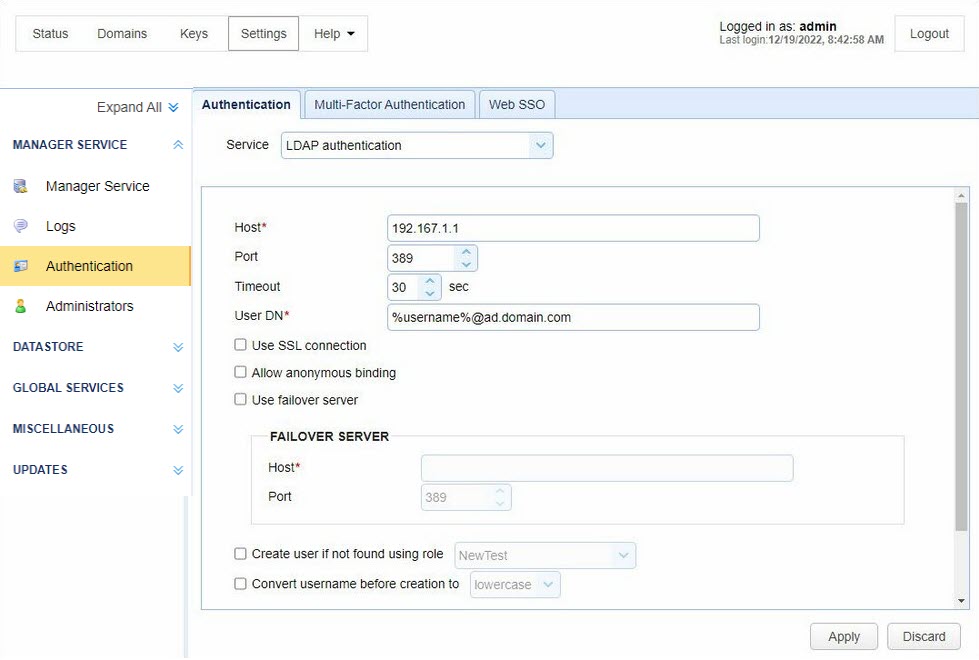
Host — Identifies the hostname or IP address of the LDAP service.
Port — Identifies the port of the LDAP service.
Timeout — Identifies the connection timeout when connecting to the LDAP service.
User DN — Identifies user Distinguished Name (DN) when authenticating with the LDAP service. The variable %username% can be used. It refers to the username passed in during the authentication process.
Use SSL connection — If selected, the connection to the LDAP server uses an SSL connection.
Allow anonymous binding — If selected, a user can bind anonymously to the LDAP directory.
Use failover server — If selected, authentication is attempted against the failover server if the primary LDAP server becomes inaccessible.
FAILOVER SERVER
Host — Identifies the LDAP failover server host.
Port — Identifies the LDAP failover server port.
Create user if not found using role — If selected, and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the user name supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the specified Role.
LDAP Query authentication lets you authenticate an Administrator based on the results of an LDAP query. This is a two-step authentication process.
-
The Admin is authenticated against the LDAP server using the
User DNfield and password supplied by the user. -
The query is performed using credentials supplied in
Search user DNandPasswordfields.The Search user DN credentials may differ from the credentials used in Step 1. A scenario where they may differ is when theUser DNdoes not have the required permissions to perform the query, but theSearch User DNdoes.
If one or more records are returned from the query, then the user is authenticated.
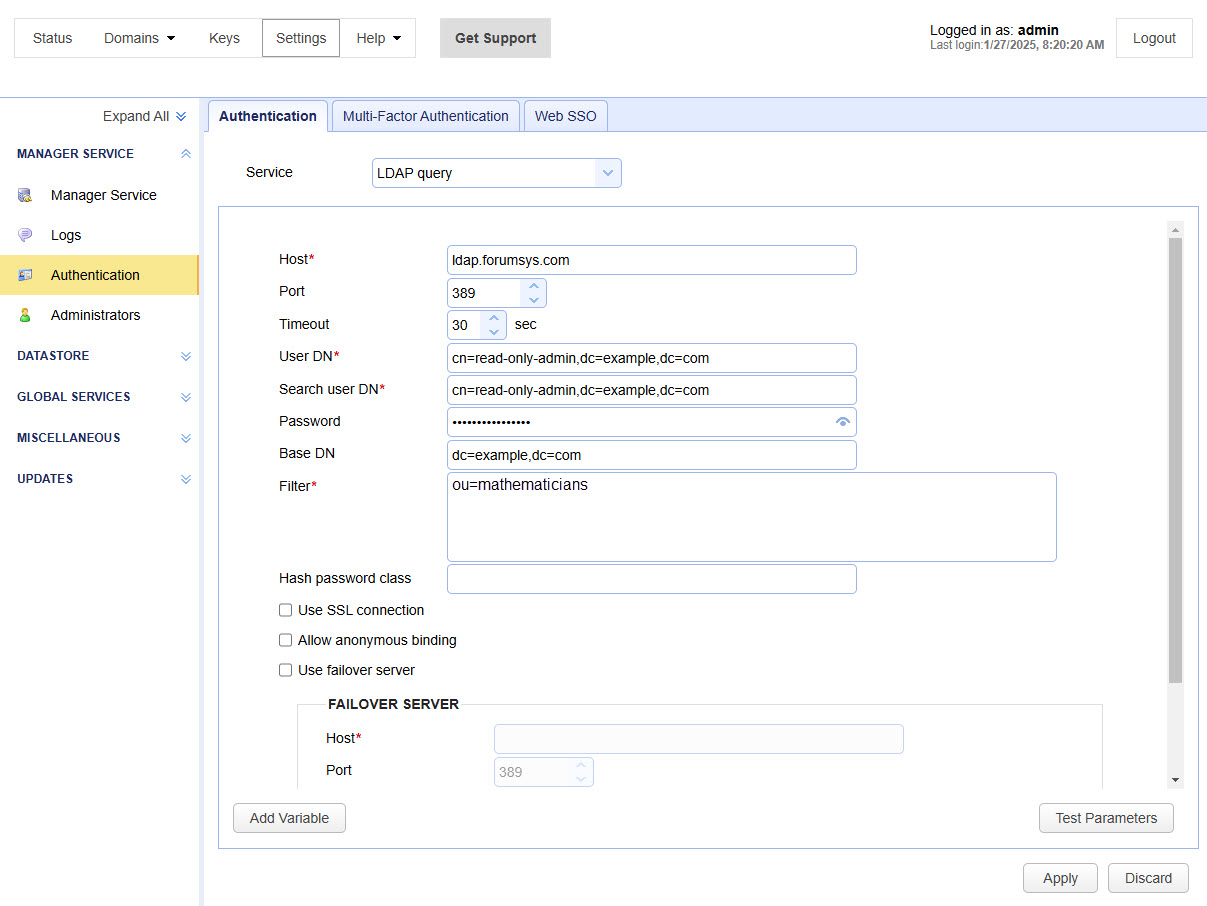
Host — Identifies the hostname or IP address of the LDAP service.
Port — Identifies the port of the LDAP service.
Timeout — Identifies the connection timeout when connecting to the LDAP service.
User DN — Identifies the user's Distinguished Name when authenticating with the LDAP service.
Search user DN — Identifies the user's Distinguished Name used for performing the LDAP search query.
Password — Identifies the user password for performing the LDAP search query.
Base DN — Identifies the base Distinguished Name in which to perform the Filter.
Filter — Identifies the filter to execute using LDAP filter syntax. There are two special variables that may be used when performing the database query: %username% and %password%. They refer to the username and password supplied by the Admin during the authentication process.
Hash password class — Identifies the Java class to use for hashing the password before passing it to Filter. The password is passed to Filter in clear text if no class is specified.
Use SSL connection — If selected, connect to the LDAP server using an SSL connection.
Use failover server — If selected, authentication is attempted against the failover server if the primary LDAP server becomes inaccessible.
FAILOVER SERVER
Host — Identifies the LDAP failover server host.
Port — Identifies the LDAP failover server port.
Create user if not found using role — If selected, and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the username supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the specified Role.
When using LDAP Query authentication, you must define a filter that is used to identify the record you are searching for. The syntax of LDAP filters are defined in RFC 2254. The table below provides a list of valid expressions and their meanings.
| Symbol | Filter | Example | Example matches |
|---|---|---|---|
|
= |
Equality |
(sn=Smith) |
Surname of Smith only. |
|
> |
Greater than |
(sn>Smith) |
Any surname that alphabetically follows Smith. |
|
>= |
Greater than or equal to |
(sn>=Smith) |
Any surname that includes or alphabetically follows Smith. |
|
< |
Less than |
(sn<Smith) |
Any surname that alphabetically precedes Smith. |
|
<= |
Less than or equal to |
(sn<=Smith) |
Any surname that includes or alphabetically precedes Smith. |
|
=* |
Presence |
(sn=*) |
All surnames (all entries with the sn attribute). |
|
=* |
Substring |
(sn=Smi*) |
Any matching substring of Smith. |
|
& |
And |
(& (sn=Smith) (cn=John) ) |
Surname of Smith and common name of John. |
|
| |
Or |
(| (sn=Smith) (sn=Jones) ) |
Surname of Smith or Jones. |
|
! |
Not |
(! (sn=Smith)) |
Surname not equal to Smith. |
NTLM authentication lets you authenticate a User against an existing Windows domain.
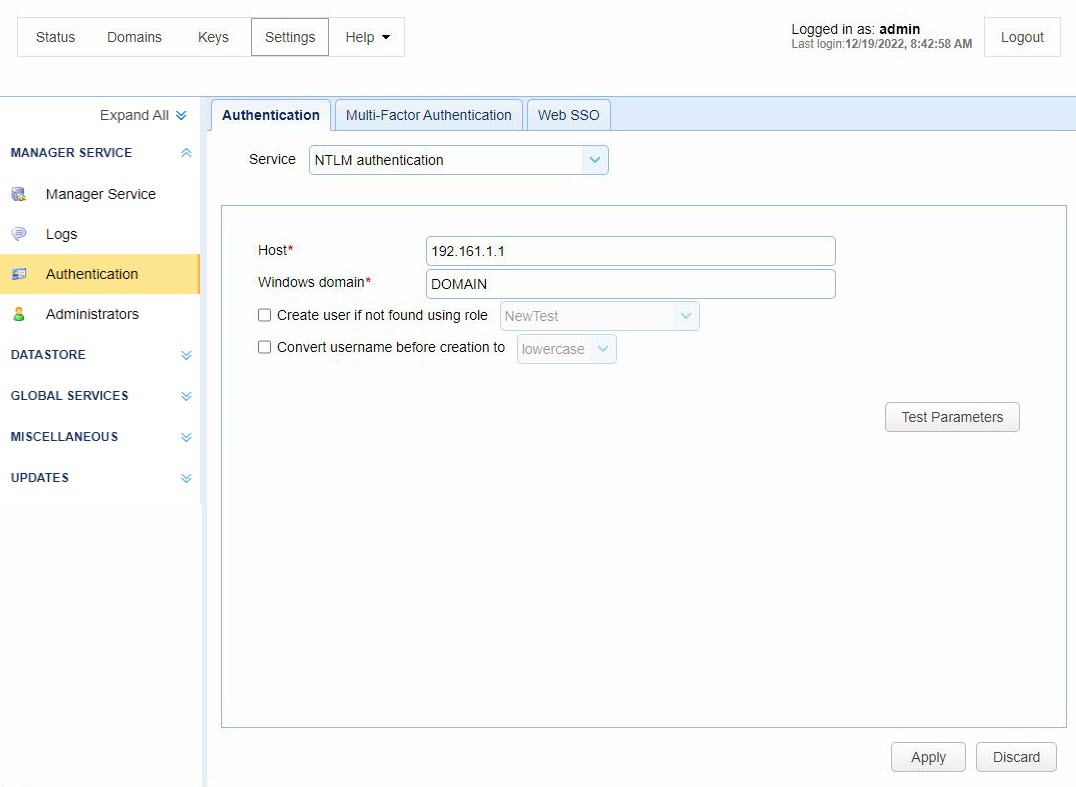
Host — Identifies the IP address of the Windows domain controller.
Windows domain — Identifies the name of the Windows domain to which the users belong.
Create user if not found using role — If selected, and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the username supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the specified Role.
PAM authentication lets you authenticate an Admin against an existing Unix PAM user repository. To use the PAM Authentication module, you must install some native libraries that allow MFT Server to communicate with your PAM user repository.
-
Download the JPam library for your operating system.
-
Copy the native library to the Java Native Library Path. See the Native Library Installation Location table for more information.
Step 1, as found in the JPam instructions, must be ignored as thejpam.jarfile already exists in thelibsdirectory of your MFT Server installation. Additionally, JPam instructions state you may optionally place the native library in the same directory as thejpam.jarfile instead of the Java Native Library Path. This is incorrect. For JPam to work with MFT Server, you must place the native library in the Java Native Library Path and not in the libs directory of MFT Server. -
Configure JPam for use by editing the
net-sf-jpamfile and copying it to the/etc/pam.ddirectory. -
Restart the MFT Server service.
-
Using the MFT Server Manager, navigate to the
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Authentication > Authenticationtab and set the Service field to PAM authentication, then enable other options. See the image below. -
Click
Test Parametersto test the connection.
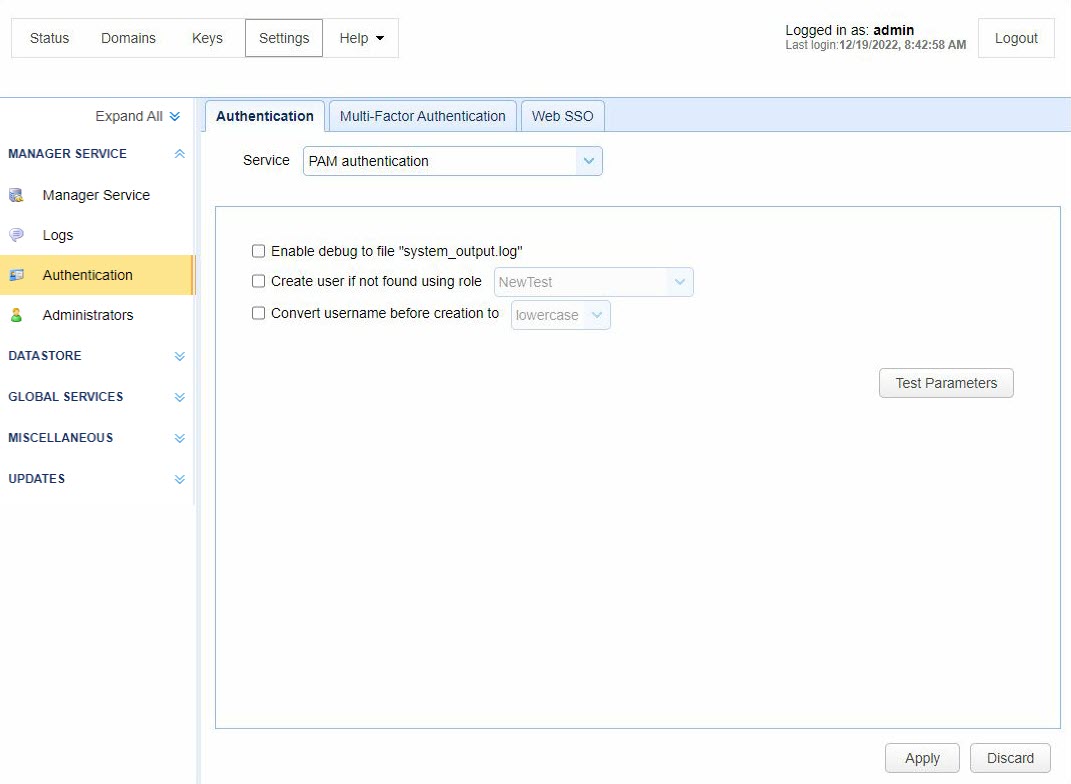
Enable debug to file system_output.log — If selected, this sends debugging information to the file system_output.log located in the installation directory.
Create user if not found using role — If selected, and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the user name supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the specified Role.
RADIUS authentication lets you authenticate an Admin against an existing RADIUS server.
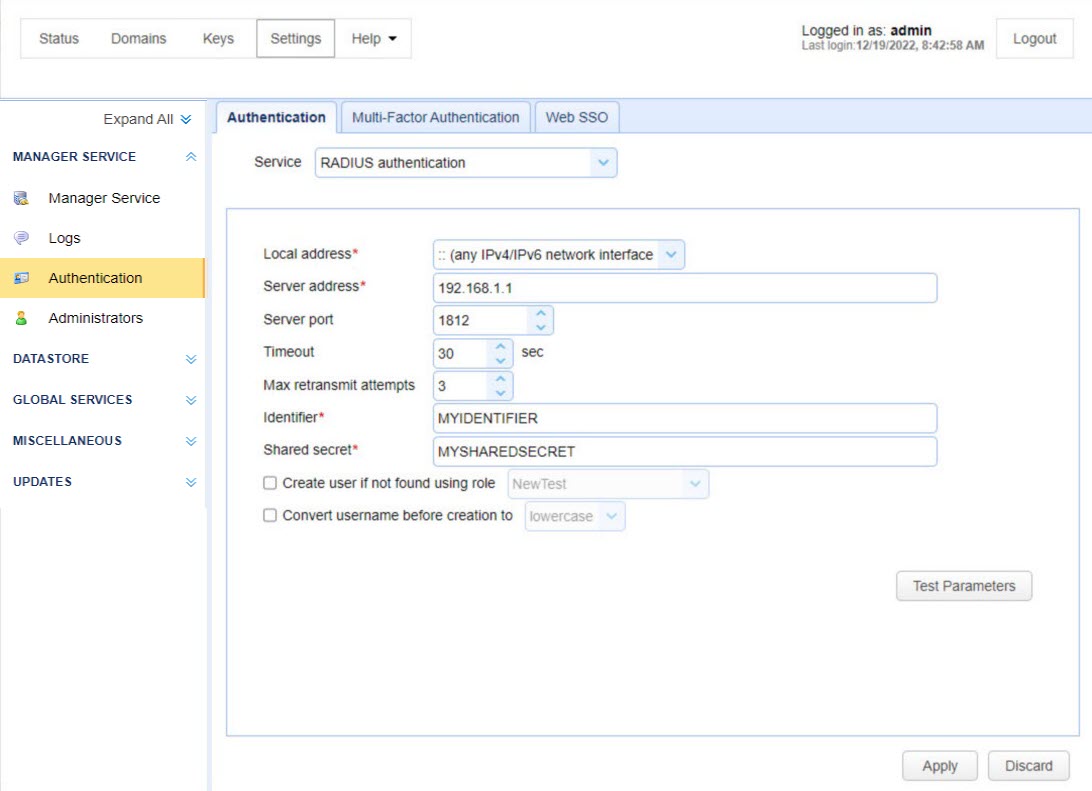
Local address — Identifies the local UDP address for socket binding.
Server address — Identifies the Radius server address.
Server port — Identifies the RADIUS server port.
Timeout — Identifies the timeout (in seconds) for connecting to the RADIUS server.
Max retransmit attempts — Identifies the maximum number of retransmission attempts when there is no response from the RADIUS server.
Identifier — Identifies the RADIUS server Identifier value.
Shared secret — Identifies the RADIUS server's shared secret value.
Create an account if not found using role — If selected and the account authenticates successfully, MFT Server automatically creates the account (using the specified Role) if the account does not already exist.
Convert username before creation to <uppercase | lowercase> — If selected, the username supplied is converted to upper or lowercase before passing the username to the specified Role.
Custom authentication lets you define your own custom authentication class to use for Admin authentication. Follow the steps below.
-
Create a class that implements the
com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.administrator.authentication.AuthenticationServiceclass. -
Overload the
public void authenticate(AuthenticationCredentials creds)method, throwing acom.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.administrator.authentication.OperationExceptionexception if authentication fails, or return the username of the Administrator if authentication passes. -
Create a JAR file that contains the compiled version of your
com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.administrator.authentication.AuthenticationServiceimplementation. To compile your authentication class you must include theftpserver.jarlibrary in your classpath. Theftpserver.jarlibrary is located in thelibsdirectory of MFT Server. -
Place the JAR file created in Step 3, and any needed 3rd party JAR files, into the
libs/extdirectory of your MFT Server installation. -
Restart the MFT Server service.
-
Open the MFT Server Manager and navigate to
Settings > MANAGER SERVICE > Authentication > Authenticationand change the Service tocustom authentication,then clickApply.
An example implementation of com.jscape.inet.mft.subsystems.administrator.authentication.TestAuthenticationService is located in the ftpserver.jar file for testing.
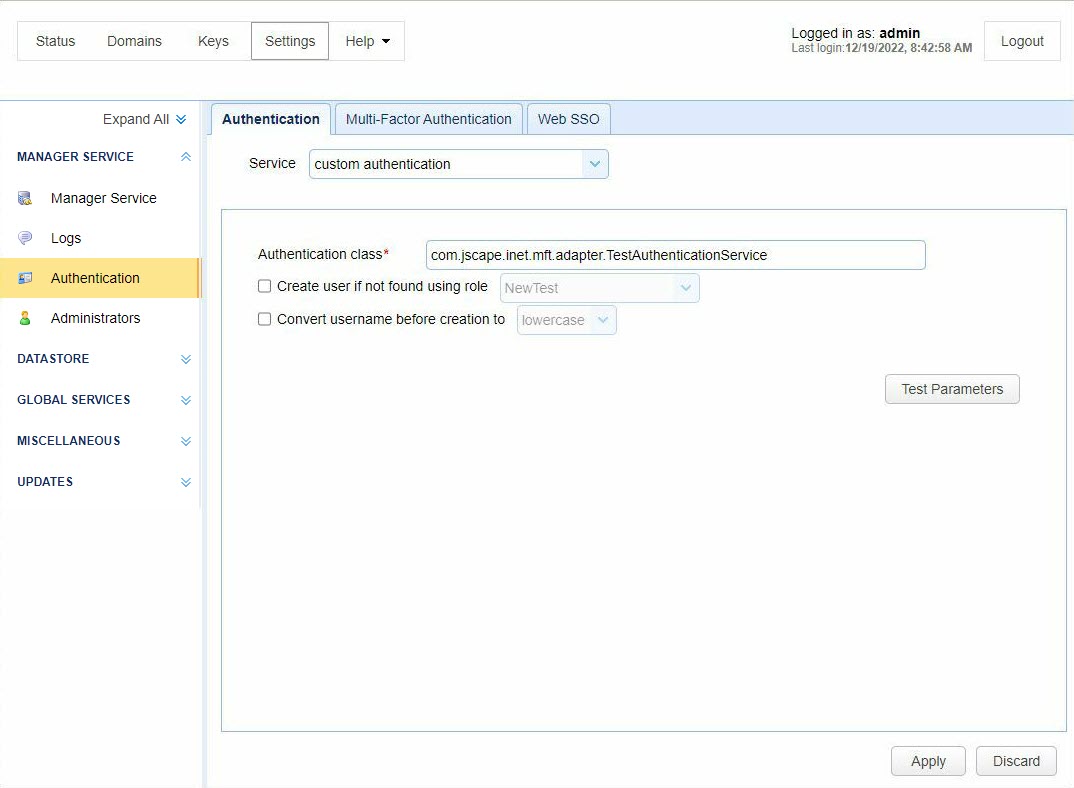
The following information is taken directly from the TestAuthenticationService example provided in ftpserver.jar library. There are two exception types that may be thrown as part of this example - UnsupportedCredentialsTypeException and InvalidCredentialsException.
-
If the
UnsupportedCredentialsTypeExceptionis thrown, MFT Server will attempt to validate the credentials against local credentials stored in MFT Server, instead of using the logic provided in custom authentication class. -
If the
InvalidCredentialsExceptionis thrown, the user is immediately denied access.
package com.jscape.inet.mft.adapter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestAuthenticationService
implements AuthenticationService {
@Override
public String authenticate(AuthenticationCredentials credentials)
throws OperationException {
if (credentials instanceof PasswordCredentials) {
return authenticate((PasswordCredentials) credentials);
} else if (credentials instanceof TokenCredentials) {
return authenticate((TokenCredentials) credentials);
}
throw new UnsupportedCredentialsTypeException(credentials);
}
private String authenticate(PasswordCredentials credentials)
throws OperationException {
assertPasswordValid(credentials.username, credentials.password, credentials);
return credentials.username;
}
private String authenticate(TokenCredentials credentials)
throws OperationException {
try {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(credentials.token).useDelimiter(":");
String username = scanner.next();
String password = scanner.skip(":").nextLine();
assertPasswordValid(username, password, credentials);
return username;
} catch (InvalidCredentialsException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new InvalidCredentialsException(credentials);
}
}
private void assertPasswordValid(String username, String password, AuthenticationCredentials credentials)
throws InvalidCredentialsException {
if (!username.equals(password)) {
throw new InvalidCredentialsException(credentials);
}
}
}
Multiple authentication lets you to authenticate Administrators using multiple authentication service types. If the first authentication type does not succeed, the next authentication type in the ordered list is used. This continues until a successful authentication occurs, or the list is exhausted and the authentication fails.
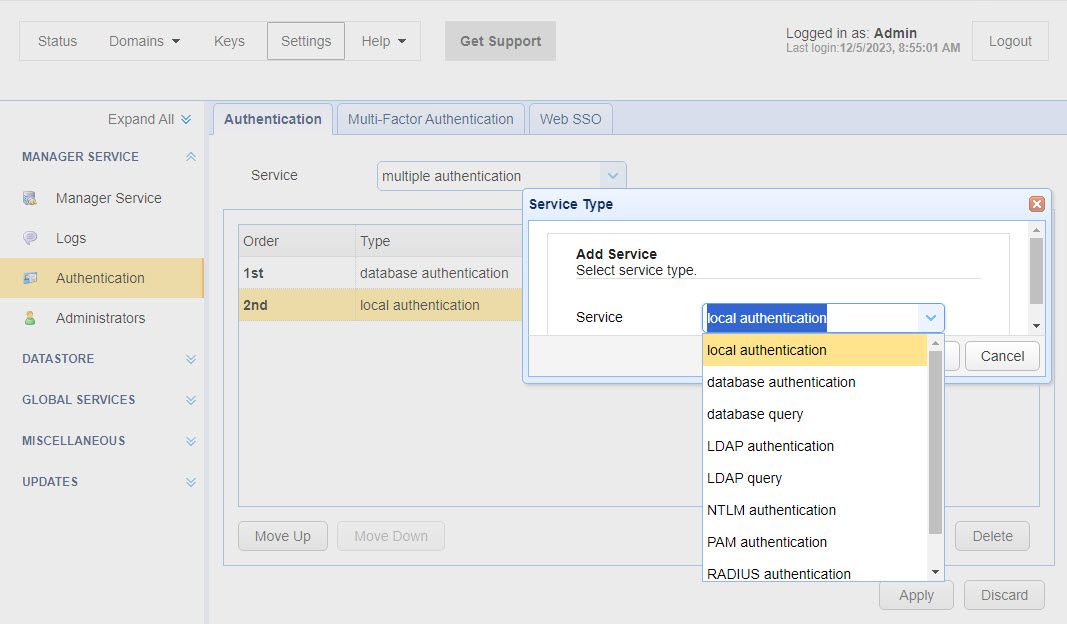
When you choose Multiple authentication, you must define at least two types of authentication. You cannot save what you enter for Multiple Authentication if you only define one authentication Service type.
Click Add (which was done in the image above) and select a service you wish to configure from the dropdown list (two are already configured in the above image). You are allowed to configure up to five authentication service types. You can use the same type more than once, using different parameters. The configuration details of each service type are the same as those described above.
When authenticating, the Admin is authenticated against the first service (the Order column displays 1st, 2nd, etc., as depicted in the image above). If authentication is successful, the Admin is granted access using the first service. If the authentication fails, a second authentication attempt is made using the second service. If successful, the Admin is granted access. If the second authentication service fails, what happens next depends on whether another service is configured. If no other service is configured, the Admin is denied access. If a third authentication service is configured, that is used next. The same pattern will continue for each service configured (up to five). The system goes down the ordered list but stops when it can authenticate the Admin. If none of the authentication services succeed, the Admin is not granted access.
Move Up and Move Down allow you to change the order of your two or more services.
IP disabling and raising the Administrator Login Trigger event, these actions occur only after all authentication methods have been attempted or a successful login is achieved.