Adding a Global FTP/S Service

FTP and FTPS (the secure version of FTP) are general-purpose file transfer protocols. They are used for performing a variety of file transfer operations like small, one-time transfers, or large bulk file transfers.
To add a Global FTP or FTPS service, navigate to the Settings > GLOBAL SERVICES > Listeners > Listeners tab and click Add. The Service Protocol dialog displays. Select FTP from the Protocol dropdown list. Click OK.
The Add "FTP/S" Global Service dialog displays, as shown in the image below.
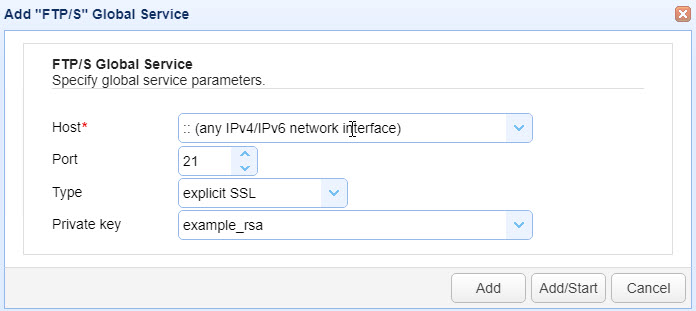
The fields are described below.
Host — Identifies the IP address the service listens on. The default value is "::" which means any available IPv4 or IPv6 IP address/network interface is used.
Port — Identifies the port that the service listens on. The default port number for explicit SSL (regular and forced) is 21. The default port number for implicit SSL is 990.
Type — Select one of the following types:
Regular — The original, non-encrypted version of FTP (plain FTP). The command (control) channel and the data channel are not encrypted. It is recommended that you use this protocol for testing purposes only.
FTPS — The secure version of FTP. It acquires its security from SSL/TLS and has 3 modes - explicit, implicit, and forced SSL.
Explicit SSL — A mode of FTPS where you choose if the data transmitted is encrypted. This mode also supports regular FTP.
Forced explicit SSL — A mode of FTPS where the command (control) channel is always encrypted, but the data channel is optionally encrypted.
Implicit SSL — A mode of FTPS where SSL/TLS encryption is implied. In this mode, both command (control) and data channels are automatically protected with SSL/TLS encryption when a connection is established between the FTPS client and your FTPS service.
Private Key — The private encryption key that FTPS uses for encrypted communications. This is sourced from the Keys module in the top menu bar.
Click Add or Add/Start.
Add — The FTP service is added to the
Settings > GLOBAL SERVICES > Listeners > Listenersgrid with a Status of stopped. Click the Start button located under the grid to start the service.
Add/Start — The FTP service is added to the
Settings > GLOBAL SERVICES > Listeners > Listenersgrid with a Status of running (if no errors are encountered).
To customize the FTP/S service, navigate to the Settings > GLOBAL SERVICES > LISTENERS > FTP/S tab. See the image below.
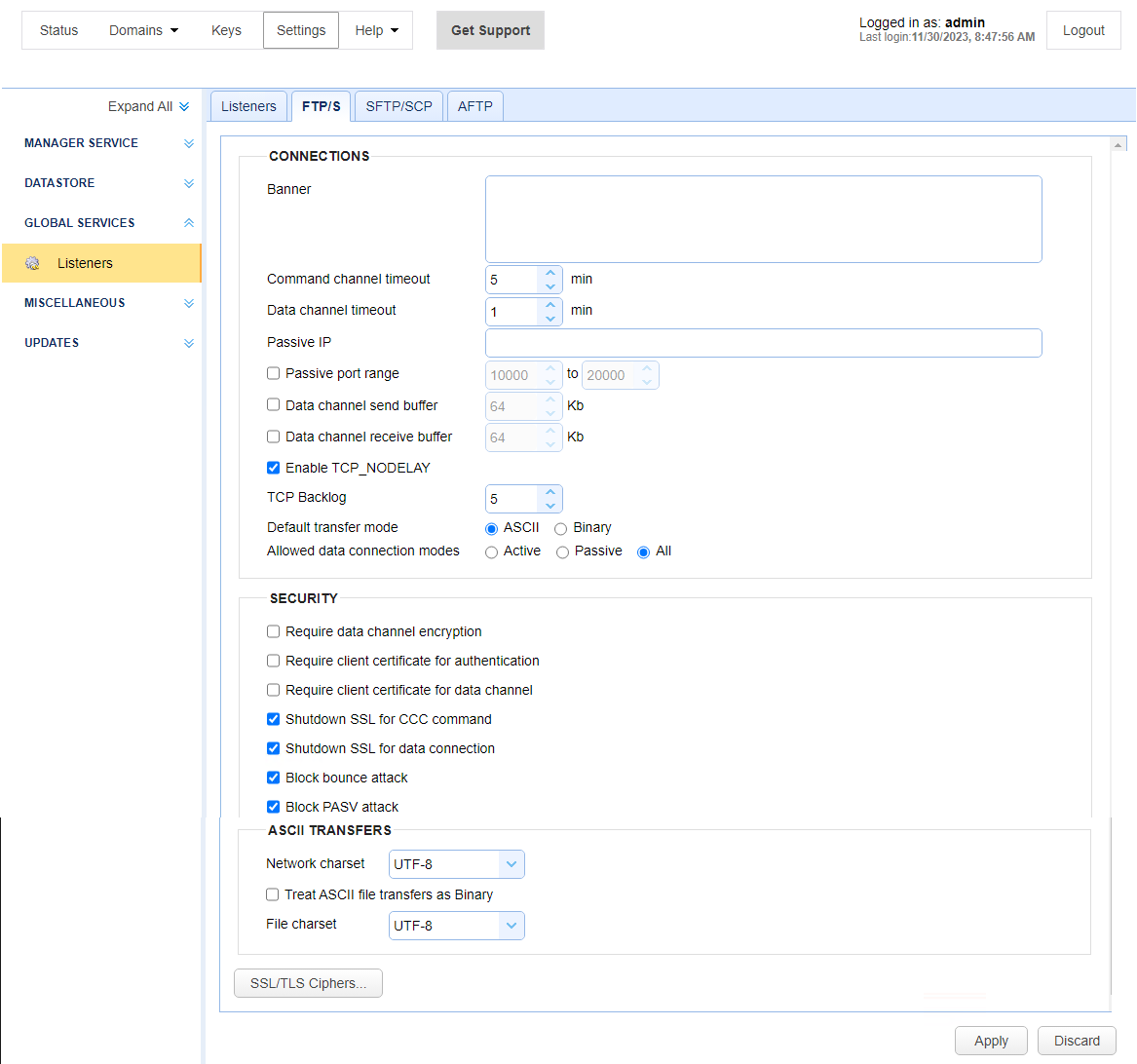
The fields are described below.
CONNECTIONS
Banner — Identifies the banner to display for FTP clients.
Command channel timeout X min — Identifies the number of minutes that a client can remain inactive on the command channel before the server forcefully disconnects them.
Data channel timeout X min — Identifies the number of minutes that a client can remain inactive on the data channel before the server forcefully disconnects them.
Passive IP — Identifies the IP used when responding to PASV client requests.
Passive port range X to Y — Identifies the server port range for servicing PASV client requests.
Data channel send buffer X KB — Identifies the size of the data channel's send buffer. The default value is the send buffer size for the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Data channel receive buffer X KB — Identifies the size of data channel's receive buffer. The default value is the receive buffer size for the JVM.
Enable TCP_NODELAY — If selected, Nagle's algorithm is disabled.
Default transfer mode <ASCII/BInary> — Identifies the default transfer mode the server uses if the client does not specify the transfer mode.
Allowed connections modes <Active/Passive/All> — Identifies the allowed connection mode or modes for file transfers and directory listings.
SECURITY
Require data channel encryption — If selected, the client is required to encrypt the data channel when using FTPS (FTP over SSL) protocol.
Require client certificate for authentication — If selected, users authenticating using FTPS (FTP over SSL) are required to authenticate using data encrypted with a private key that maps to a server-installed client certificate.
Require client certificate for data channel — If selected, users requesting data transfer using FTPS (FTP over SSL) are required to supply data encrypted with a private key that maps to a server-installed client certificate.
Shutdown SSL for CCC command — If selected, the client must properly shutdown SSL command channel connections when issuing a CCC command.
Shutdown SSL for data connection — If selected, the client must properly shutdown SSL data connections.
Block bounce attack — If selected, the FTP/S services are only allowed to make PORT requests to the originating host.
Block PASV attack — If selected, users are only allowed to connect to passive data ports that are initiated by the same client on the command channel.
ASCII TRANSFERS
Network charset — Identifies the character encoding used to transfer file names and file contents.
Treat ASCII file transfers as binary — If selected, ASCII files are transferred in binary mode.
File charset — Identifies the character encoding used to transfer file contents.
SSL/TLS Ciphers — The SSL/TLS ciphers to enable for FTPS (FTP over SSL) services. See SSL/TLS Ciphers